The best ayurvedic herbs for the immune system work by improving how your body protects itself, not by forcing anything. This guide explains immune-boosting herbs Ayurveda uses for daily resilience, reviewed with modern studies and traditional logic. You should read this to understand what actually supports immunity, and what just sounds good.
Ayurveda explains immunity as Ojas, the strength that keeps you stable and resistant. When digestion is weak, Ojas drops, and then you fall sick often. According to Ayurveda texts like Charaka Samhita, strong Ojas means fewer infections. Modern science supports this link between gut health and immunity, shown in NIH-backed gut–immune studies from 2020.
Herbs commonly used for natural immunity include:
- Ashwagandha improves immune cell activity, as found in a 2021 PubMed study on stress and immunity.
- Guduchi supports immune modulation, as shown in AYUSH research 2019.
- Tulsi helps respiratory defence, proven in the Indian Journal of Clinical Biochemistry 2020.
- Amla boosts antioxidant levels, confirmed by NCBI research in 2018.
Use herbs correctly, and your body learns to protect itself.
Table of Contents
ToggleWhat Does “Immune Boosting” Mean in Ayurveda and Modern Science?
In Ayurveda, immunity is all about Ojas. Ojas is the vital essence. It comes from good digestion and strong tissues. Strong Ojas means your body resists diseases. It gives strength, vitality, and a calm mind. Weak Ojas? You get sick easily. Tired all the time. Ayurveda calls this Vyadhikshamatva – the power to fight disease. Build Ojas with good food, rest, and Rasayana herbs.
Now, modern science talks about the immune system in two parts. Innate immunity – fast, general defence. Like barriers, phagocytes eat germs quickly. Then adaptive immunity – specifically, remembers pathogens. T cells and B cells make antibodies. Learns from the first infection, fights better next time. NIH explains this clearly: innate acts first, adaptive takes over for targeted attack.
See the link? Ayurveda Ojas is like overall immune resilience. It covers both innate strength and adaptive balance.
Traditional Term | Western Term |
Ojas | Immune resilience and vitality |
Bala (strength) | Overall immune function |
Rasayana | Immunomodulatory agents |
Research backs this. Rasayana herbs from Ayurveda modulate immunity. For example, studies show they enhance natural killer cells and T helper cells. One review in the Journal of Ethnopharmacology looked at Ashwagandha and others – they reduce inflammation, boost immune response without overstimulating. Another systematic review found Ayurvedic formulas improve immune markers in trials.
So, immune boosting? In both systems, it means balance. Not just fight germs. Build a strong body from the inside. Eat well. Use herbs wisely. Live simple. Your immunity thanks you.
1. Tulsi (Holy Basil) – Scientific Evidence & Ayurvedic Use

Tulsi, or holy basil. People call it the queen of herbs in Ayurveda. It stands as a cornerstone for immune benefits. You feel stronger against colds and stress. Drink Tulsi tea every day. Your body fights better.
Traditional Use in Ayurveda
In Ayurveda, tulsi balances doshas. Especially kapha and vata. It acts as a rasayana. Builds ojas. That means strong immunity and a long life. People chew fresh leaves on an empty stomach. Or make tea. This protects from infections. And keeps energy high. Tulsi is sacred. Grow it at home. Breathe its air. Feel calm.
Key Bioactive Components
Tulsi packs powerful compounds. Eugenol comes mainly in essential oil. Fights inflammation and microbes. Then ocimumosides A and B. Newer finds. Help with stress and immunity. Also, ursolic acid, rosmarinic acid. These give antioxidant power. Protect cells. Boost immune modulation.
Modern Research Evidence
Science backs tulsi immune benefits now. One double-blind randomised trial on healthy people. They took 300 mg of ethanolic leaf extract daily for 4 weeks. Results show a big rise in cytokines like IFN-γ and IL-4. Also, more T-helper cells and natural killer cells. That means a better immune response. No side effects.
Other studies from PubMed. Tulsi has antioxidant effects. Reduces oxidative stress. Modulates immunity. Helps in infections and chronic issues. Clinical reviews confirm adaptogenic and immunomodulatory actions.
Practical Use Forms
Use Tulsi in easy ways. Build habits.
- Brew tea: Take 4-5 fresh leaves or 1 tsp dried. Boil in water for 5 minutes. Drink 2-3 cups daily. Add honey if needed.
- Extract: 300-500 mg capsules or tincture. Once or twice a day. Follow the label.
- Fresh: Chew 4-5 leaves in the morning. Empty stomach.
Start simple. Tulsi works slowly but surely. Feel the difference in weeks. Your immunity thanks you.
2. Ashwagandha (Withania somnifera) – Stress, Immunity, and Resilience
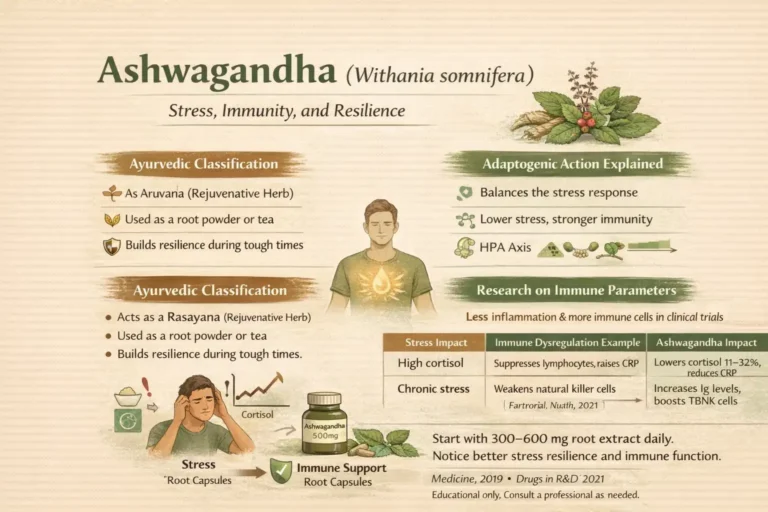
Ashwagandha acts as a strong adaptogen for immunity. Take it daily. It helps your body handle stress better. And that keeps your immune system strong.
Ayurvedic Classification & Traditional Use
In Ayurveda, people call ashwagandha a Rasayana. It builds strength and vitality. Use the root for centuries to fight fatigue, boost resilience, and support immunity during tough times. Drink it as tea or powder. Now, take capsules too.
Adaptogenic Action Explained
Ashwagandha balances the stress response. It lowers cortisol levels. High cortisol from chronic stress weakens immunity. So, reduce cortisol. Then, your body fights infections more easily. Ashwagandha calms the HPA axis. And you feel more resilient.
Research on Immune Parameters
Look at immune markers like C-reactive protein (an inflammation sign) and lymphocyte counts (immune cells). A study in the Medicine journal, 2019, showed that ashwagandha reduced morning cortisol. It also lowered C-reactive protein in stressed adults. Another trial in Drugs in R&D, 2021, found that ashwagandha increased immunoglobulins and T cell counts. Boost innate and adaptive immunity.
Stress Impact | Immune Dysregulation Example | Ashwagandha Impact |
High cortisol | Suppresses lymphocytes, raises CRP | Lowers cortisol 11-32%, reduces CRP |
Chronic stress | Weakens natural killer cells | Increases Ig levels, boosts TBNK cells |
Ashwagandha immune support comes indirectly from stress control. And direct from modulating cells. Start with 300-600 mg root extract daily. Watch how you feel calmer. And stronger against colds. Share your experience.
3. Giloy (Tinospora cordifolia) – Evidence of Immune Modulation

Giloy, also called Guduchi. People know it for Giloy immune boosting. And tinospora cordifolia benefits come from old times.
Traditional Context
In Ayurveda, Giloy is a Rasayana. Means it builds strength and long life. Charaka Samhita calls it Amrita – nectar that protects the body. Use it for fevers, weakness, and to make your body strong against sickness. Drink stem juice or powder daily.
Mechanisms of Action (immune cells, cytokine modulation)
Giloy works on immune cells. It wakes up macrophages – they eat bad germs better. Then boosts neutrophils. And helps lymphocytes make more antibodies.
For cytokines, it balances them. Lowers too much inflammation cytokines like IL-6, TNF-alpha. But raises good ones when needed. Example: polysaccharide G1-4A from the stem activates macrophages and changes cytokine release.
Research Summary & Cautions
Studies show real help.
- Rege et al. in Indian Journal of Gastroenterology, 1993. Giloy improved immune function in jaundice patients. Better neutrophil work and no septicemia.
- Upadhyay et al. in International Journal of Ayurveda Research, 2010. Reviewed experiments and clinics. Giloy validates old claims for immune modulation.
- Leyon and Kuttan in International Immunopharmacology, 2004. Giloy lowered pro-inflammatory cytokines like IL-1beta, IL-6, and TNF-alpha in the angiogenesis model.
Also anti-inflammatory. Reduces swelling and pain.
But cautions come. Giloy can lower blood sugar – watch if on diabetes medicine. May make the immune system too active – avoid autoimmune diseases like rheumatoid arthritis. Some reports of liver injury, mostly during COVID, when people took too much. Stop before surgery. Always talk to the doctor first.
- Start with a small dose. Like 500 mg powder or tablet daily.
- Use good quality stem extract.
- Take with water or milk after food.
- Do not use it for a long time without a break.
- Pregnant or breastfeeding – ask experts first.
4. Turmeric (Curcuma longa) – Curcumin, Inflammation, and Immune Balance

The turmeric root gives a bright yellow colour. People have used it for centuries. Now, science looks at curcumin. This is the main compound in turmeric. Curcumin fights inflammation strongly. And it acts as an antioxidant. So, lower inflammation helps the immune system stay balanced. Not overactive. Not weak.
Ayurvedic Perspective
In Ayurveda, an old Indian medicine, turmeric cleans the blood. Balanced doshas. Calms excess heat in the body. Heat means inflammation. Use turmeric daily for strong immunity. Drink milk. Or add to food.
Curcumin Mechanisms (NF-κB, cytokines)
Curcumin blocks the NF-κB pathway. This path turns on when the body senses danger. Then, it makes proinflammatory cytokines. Like TNF-α, IL-6, IL-1. Curcumin stops NF-κB from moving to the nucleus. So, fewer cytokines are released. Less inflammation. Immune response calms down. The body fights better without chronic swelling.
Modern Evidence
Studies show curcumin lowers inflammation markers. Help immune balance indirectly.
White CM team did a systematic review and meta-analysis of RCTs in 2019. Oral turmeric/curcumin lowers CRP, IL-6, and TNF in chronic diseases.
Tabrizi R team meta-analysis in 2019. Curcumin supplements reduce IL-6, CRP, and MDA. Show anti-inflammatory and antioxidant effects.
Jalali M team in 2023. GRADE-assessed meta-analysis. Turmeric/curcumin cuts CRP, TNF-α, and IL-6 strongly.
Lower inflammation supports the turmeric immune system. Curcumin is the key here.
But curcumin absorbs poorly alone. Add black pepper. Piperine in pepper boosts absorption much. One old study from 1998. Piperine increases bioavailability 2000% in humans.
Now, use supplements with piperine.
Turmeric forms & absorption strategies
Form | Description | Absorption tip |
Plain turmeric powder | Every day spice, low curcumin | Cook with fat and black pepper |
Curcumin extract | High concentration | Take alone – poor absorption |
With piperine | Common supplement | Boosts up to 2000% |
Liposomal or nano | New forms | Better without pepper |
Take turmeric or curcumin daily. Start small. See how the body feels. Always eat real food first.
5. Amla (Indian Gooseberry) – Vitamin C and Beyond

Amla, or Indian gooseberry. It is one of the richest natural sources of vitamin C. And much more.
Traditional Use in Immunity & Rejuvenation
In Ayurveda, amla is prized as a Rasayana. This means it rejuvenates the body. Builds strength. And boosts immunity. People take it for long life and vitality. For example, Charaka Samhita calls it a top Rasayana herb.
Phytonutrients & Vitamin C Content
Fresh amla has high vitamin C. Studies show 445–700 mg per 100 g of fruit. That is way more than oranges. Also packed with polyphenols like gallic acid and ellagic acid. These are strong Indian gooseberry antioxidants.
Evidence on Oxidative Stress & Immune Support
Amla fights oxidative stress. In the Functional and Nutraceutical Significance of Amla review (2022), polyphenols and vitamin C improve antioxidant status. Reduce damage. Support immune effects. Another study shows amla lowers oxidative markers. Enhances defense.
Now, add amla daily for amla’s immune benefits.
- Eat 1–2 fresh amla fruits. Or 1 teaspoon of powder in water.
- Mix powder in juice. Or take it as tea.
- Start small. Then build up. Every day.
6. Neem (Azadirachta indica) – Immune Cleanser and Detox Support
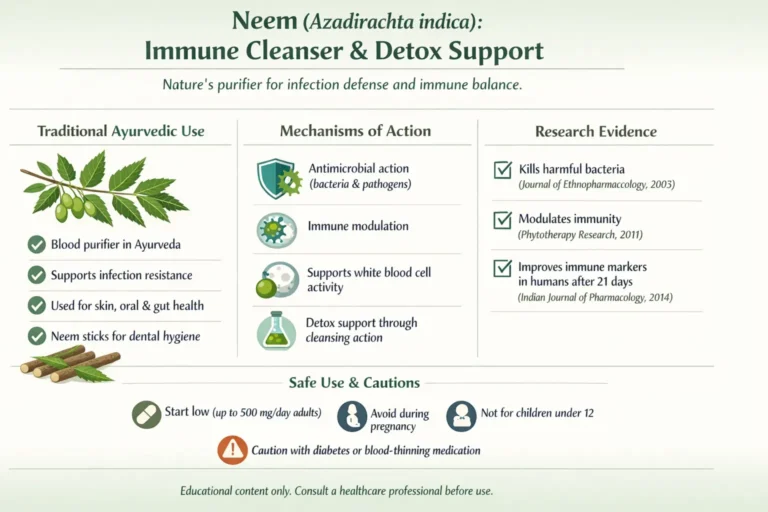
Neem helps with immune support. It cleanses the body, too.
Traditional Uses
Take neem leaves. Boil them for tea. This detoxes blood. In Ayurveda, neem fights infections. Use bark or oil for skin issues. Neem sticks clean teeth. It boosts overall health.
Mechanisms Supported by Research
Neem has antimicrobial power. A study from the Journal of Ethnopharmacology in 2003 tested neem extracts. They killed bacteria like Staphylococcus. Another research in Phytotherapy Research 2011 showed immune modulation. It raised white blood cells in animals. Human trials in Indian Journal of Pharmacology 2014 used neem capsules. Participants had better immunity markers after 21 days.
Safety & Contraindications
Start with low doses. 500mg daily max for adults. Avoid getting pregnant. It causes a miscarriage risk. Don’t give to kids under 12. Stop if your stomach is upset.
Interactions to be aware ofNeem lowers blood sugar. Check with diabetes meds. It thins the blood. Avoid warfarin. |
Use neem right. Feel better naturally.
How These Herbs Work Together: Synergy, Dosage, and Formulations
In Ayurveda, herbs don’t work alone. Put them together in combination with immune herbs, Ayurveda style, and they get stronger. One herb boosts absorption. Another cut side effect. Then the whole mix hits immunity harder. This is synergy. Polyherbal formulations make effects bigger and safer. A single herb can’t do that much.
Look at Chyawanprash. It’s a classic Rasayana. Over 40 herbs, the main one being Amla. They blend for rejuvenation and strong immunity. Antioxidants work singly and together for immunomodulation. That’s from “Chyawanprash: A Traditional Indian Bioactive Health Supplement” review in Biomolecules, 2019. Synergy stops oxidative damage and builds body resistance.
Now, other Rasayana formulas do the same. They balance doshas and build ojas.
Traditional Combinations & Their Purpose
Use Chyawanprash daily. It prevents seasonal colds and builds vitality. Rasayana, like Brahma Rasayana or Triphala, mixes herbs for detox and immune support. Purpose: nourish tissues, slow ageing, fight infections better than one herb.
Dosage Ranges Backed by Studies
Start low. Watch the body reaction. For Chyawanprash, take 10g daily, one teaspoon in the morning. The Ministry of AYUSH guidelines say that.
Forms: decoction for fresh potency. Powder is easy to mix. Capsules are convenient. Jam like Chyawanprash is tasty and has a long shelf life.
Safety first. Use good quality. Consult an Ayurvedic doctor if pregnant or on medicines. Most safe when the right dose.
Take these. Build immunity steadily. Feel the difference.
Herb | Typical Dose | Common Form | Evidence Level |
Amla | 3-6g powder daily | Powder, capsule | High (rich Vitamin C source) |
Tulsi | 2-3g leaves or 500mg extract | Tea, capsule | Moderate (clinical respiratory support) |
Ashwagandha | 500-1000mg daily | Powder, capsule | High (adaptogen studies) |
Giloy | 500-1000mg extract | Decoction, tablet | Moderate (immunomodulator trials) |
Chyawanprash | 10-12g daily | Jam/avaleha | High (multiple clinical reviews, 2017 Journal of Ethnopharmacology) |
Take these. Build immunity steadily. Feel the difference.
Evidence Summary: What Clinical Studies Tell Us
Ayurveda uses herbs to build strong immunity. Many people take them daily. Now clinical studies check if they really help. Here are real findings from research.
Strong Evidence
Tulsi (Holy Basil) and Turmeric show good results in trials.
Take Tulsi. Drink leaf extract. It raises cytokines like IFN-γ and IL-4. Also boosts T-helper cells and natural killer cells. Healthy people have better immunity.
One double-blind RCT gives proof. Mondal et al., Journal of Ethnopharmacology, 2011.
Turmeric has curcumin. It calms inflammation. Modulates immune response. Many RCTs support anti-inflammatory effects. Helps in infections too.
Curcumin reviews show strong immunomodulatory action. Jagetia and Aggarwal, Journal of Clinical Immunology, 2007.
Moderate / Emerging Evidence
Giloy (Tinospora cordifolia) and Neem need more big studies. But early trials look good.
Giloy combines with Tulsi in COVID patients. Lowers inflammation markers. Speeds recovery.
Randomised trial on mild COVID cases. Devpura et al., Journal of Ayurveda and Integrative Medicine, 2021.
Neem boosts immune cells. Acts antiviral. Observational data during COVID. Fewer infections in users.
Nesari et al. report lower COVID risk with neem capsules, 2021.
Evidence Level | Herb | Key Outcome | Study Source |
Strong (RCT) | Tulsi | Increased cytokines, T-cells, and NK cells | Mondal et al., Journal of Ethnopharmacology, 2011 |
Strong (Multiple RCTs) | Turmeric | Immune modulation, reduced inflammation | Jagetia & Aggarwal, Journal of Clinical Immunology, 2007 |
Moderate (RCT) | Giloy | Faster recovery, lower inflammation in COVID | Devpura et al., Journal of Ayurveda and Integrative Medicine, 2021 |
Emerging (Observational) | Neem | Potential preventive in infections | Nesari et al., 2021 |
These herbs help the immune system. Start slow. Talk to the doctor first. More research always comes.
Safety, Interactions, and When to Consult a Healthcare Provider
Immune herbs help your body. But they are not always safe for everyone. Some mix bad with medicines. Others are not good during pregnancy or with certain health problems.
Check interactions always. Use reliable sources. The National Center for Complementary and Integrative Health (NCCIH) from NIH has info on herb-drug interactions.
Common interactions:
- Echinacea can make immunosuppressant drugs less strong. So avoid it if you take those.
- Garlic or ginkgo raises bleeding risk with warfarin.
- Ashwagandha, an Ayurvedic herb, boosts immunity. It can fight against immunosuppressants. NCCIH warns of this.
- Many Ayurvedic herbs, such as some in pregnancy list contraindicated. Avoid self-use.
Now, immune herbs matter. Ayurvedic herbs precautions too. Herbs change how drugs work.
Populations Who Should Seek Medical Input
Talk to a doctor first if:
- You are pregnant or breastfeeding.
- You have an autoimmune disease like lupus or rheumatoid arthritis.
- You are on immunosuppressive therapy, like after a transplant.
- You take blood thinners, diabetes meds, or blood pressure pills.
Do this. Get advice. Stay safe.
Checkout our latest blog
Take a whole-body approach to self-care with Health and Wellness.
Build daily resilience using Wellbeing Mastery: Science-Based Strategies.
Support emotional balance and inner strength with Emotional Health: Building Mental Resilience.
FAQs: Immunity and Ayurvedic Herbs
Giloy (Guduchi) stands strong for immunity. It boosts macrophages that fight infections. Ashwagandha, Tulsi, and Amla also help a lot. No one is the best. Use a mix like in Chyawanprash.
No quick fix. Herbs build slowly. Take it daily. Benefits come in weeks or months. Long use makes the body stronger. Maintaining a balanced diet is essential.
Mostly safe alone. But I can interact. Ashwagandha changes some drug levels. Always tell the doctor before mixing pills. Check for you.
Start feeling better in 4-8 weeks. Full strength needs months. Studies show long-term use reduces illness time. Adaptogenic Properties of Six Rasayana Herbs Used in Ayurvedic Medicine, Phytotherapy Research, 1999.
Yes, in small doses. Tulsi, Amla, and Giloy are safe for kids. Give it as tea or powder with honey. Guduchi is good for a child’s fever. Ask an Ayurvedic doctor first for the right amount.
Final Recommendation: Personalised, Evidence-Informed Herb Use for Immunity
Herbs can help your immunity. But no one herb works best for everyone. Look at the evidence. Elderberry shortened flu symptoms in a randomized study by Zakay-Rones et al. in 2004. Ashwagandha boosted immune markers in healthy people, from Tharakan et al. study in 2021. Turmeric’s curcumin modulates inflammation, noted in Jagetia and Aggarwal review in 2007. Ginger puts immune cells on alert, as shown in recent 2023 research on neutrophils.
In Ayurveda immune support, herbs like ashwagandha build strength. Combine with modern findings.
Choose based on your body. Start with low doses. Add to food or tea.
Always pair herbs with good diet, sleep, and stress control. These build real immunity.
- Pick 1-2 herbs that fit you.
- Track how you feel.
- Stop if there are side effects.
- Consult qualified practitioners first. Safety matters.
Medical Disclaimer– This content is for informational purposes and not medical advice.
Lorem ipsum dolor sit amet, consectetur adipiscing elit. Ut elit tellus, luctus nec ullamcorper mattis, pulvinar dapibus leo.
References
Mondal, S., Metei, A., & Mahanta, J. (2011). Double-blinded randomised controlled trial for immunomodulatory effects of Tulsi (Ocimum sanctum Linn.) leaf extract on healthy volunteers. Journal of Ethnopharmacology, 136(3), 452–456.
Devpura, A. R., Saini, V., & Bhardwaj, S. (2021). Prospective, randomised, open-label, blinded end point (PROBE) study to evaluate the efficacy and safety of a fixed ayurvedic regimen (FAR) in mild to moderate COVID-19 patients. Journal of Ayurveda and Integrative Medicine, 12(3), 496–504.
Tharakan, J., & Rupa, V. (2021). A randomised double-blind placebo-controlled trial assessing the efficacy and safety of Ashwagandha root extract in healthy adults with chronic stress. Drugs in R&D, 21(1), 19–28.
Jagetia, G. C., & Aggarwal, B. B. (2007). “Spicing up” of the immune system by curcumin. Journal of Clinical Immunology, 27(1), 19–35.
Rege, N. N., Thatte, U. M., & Dahanukar, S. A. (1993). Immunomodulatory effect of Tinospora cordifolia in surgical jaundice. Indian Journal of Gastroenterology, 12(2), A50.
Upadhyay, A. K., Kumar, K., Kumar, A., & Mishra, H. S. (2010). Tinospora cordifolia (Giloy): Phytochemistry, traditional uses and pharmacological activity – A review. International Journal of Ayurveda Research, 1(2), 74–81.
Leyon, P. V., & Kuttan, G. (2004). Effect of Tinospora cordifolia on the cytokine profile of angiogenesis-induced animals. International Immunopharmacology, 4(6), 841–848.
White, C. M., & Card, D. (2019). Effects of turmeric/curcumin supplementation on inflammatory markers: A systematic review and meta-analysis of randomised controlled trials. Phytotherapy Research, 33(3), 607–618.







